Mice are small, elusive creatures that often find their way into homes and businesses, causing trouble and sometimes damage. If you’ve ever wondered what keeps their populations in check, this blog will provide an insightful look into what eats mice, including natural predators and standard methods for managing a mouse problem.
Find Out What Animals Eats Mice Below!
Natural Predators of Mice
- Owls: Owls are perhaps the most well-known predators of mice. With their excellent night vision and silent flight, they are perfectly adapted to hunting small rodents. Barn owls, in particular, are effective at controlling mice populations. They use their keen hearing to locate mice in the dark and can consume several mice in one night.
- Hawks and Eagles: Birds of prey like hawks and eagles are formidable hunters. They have sharp talons and powerful beaks that make short work of mice. These birds often hunt from high perches, scanning the ground for movement. When they spot a mouse, they swoop down with incredible speed and precision.
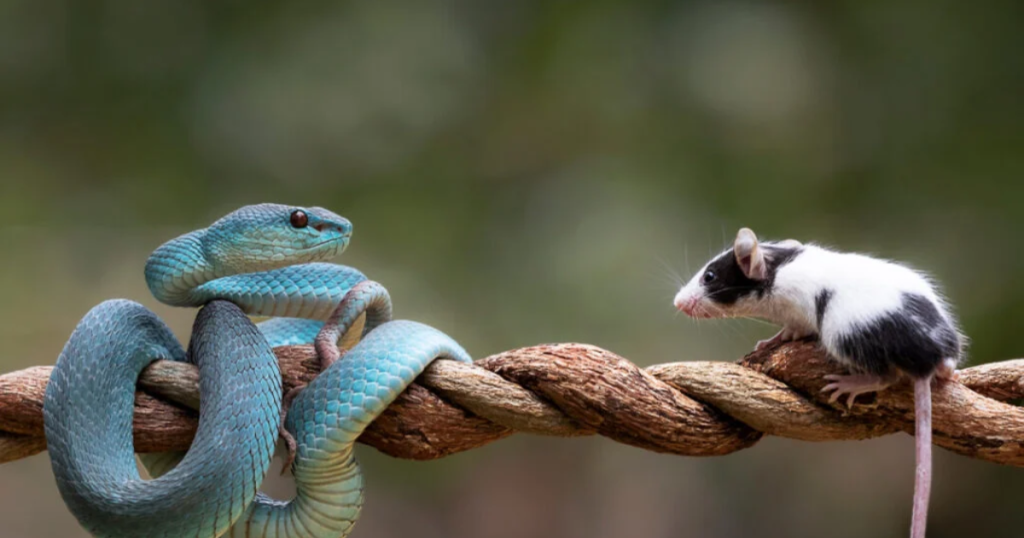
- Snakes: Many species of snakes feed on mice. For example, the common garter snake and the rat snake are known to hunt and eat mice. Snakes use their ability to slither silently and strike quickly to catch their prey. Some larger snake species, such as pythons, can consume multiple mice in one meal.
- Foxes: Foxes are versatile predators and will eat a variety of animals, including mice. They use their sharp senses of sight and smell to track down mice. Foxes are particularly effective in rural areas where they can roam freely and hunt for their next meal.
- Cats: Domestic cats have been hunting mice for thousands of years. Their playful nature often disguises their predatory skills. Cats use their agility and sharp claws to catch mice, and their presence alone can sometimes deter mice from invading homes. Many people keep cats specifically for this reason.
- Weasels: Weasels are small but fierce predators that can take down prey much larger than themselves. They are highly agile and have a high metabolism, requiring them to eat frequently. Their speed and tenacity make them excellent hunters of mice and other small rodents.
- Coyotes: Coyotes are adaptable predators found across North America. They have a varied diet that includes mice, which are a significant part of their diet in some areas. Coyotes use their keen sense of hearing and smell to locate mice and are skilled at hunting them in different environments.
Standard Methods for Managing Mouse Populations
While natural predators play a crucial role in controlling mice, there are several human methods for managing and preventing mouse infestations.
- Traps: Traps are one of the most common and effective ways to control a mouse problem. There are different types of traps, including snap traps, live traps, and glue traps. Snap traps are designed to kill mice quickly, while live traps allow for the capture and release of mice. Glue traps capture mice by sticking them to a sticky surface, but they are considered less humane.
- Bait Stations: Bait stations are designed to attract and kill mice using poison. These stations are placed in areas where mice are active, and the bait inside is toxic to rodents. However, caution is necessary when using poison, especially in homes with pets or children.
- Ultrasonic Repellents: Ultrasonic repellents emit high-frequency sounds that are unpleasant to mice but inaudible to humans. These devices are designed to drive mice away from specific areas. While the effectiveness of ultrasonic repellents can vary, they offer a chemical-free option for mouse control.
- Seal Entry Points: Preventing mice from entering your home or business is an effective way to manage their population. Sealing cracks, gaps, and holes around doors, windows, and foundations can help keep mice out. Regularly inspecting and maintaining your property can prevent new entry points from forming.
- Maintain Cleanliness: Mice are attracted to food sources and clutter. Keeping your environment clean and storing food in sealed containers can help reduce the attraction of mice. Regular cleaning and maintenance of your living space can make it less appealing for rodents.
- Professional Pest Control: For severe infestations, hiring a professional pest control service might be necessary. Pest control experts have access to advanced techniques and treatments that can effectively address large or persistent mouse problems. They can also provide advice on preventive measures to avoid future issues.
Conclusion
Understanding what eats mice helps us appreciate the natural balance of ecosystems where these small rodents play a part. From owls and hawks to snakes and foxes, various predators contribute to keeping mouse populations in check. For those dealing with a mouse problem, combining natural predator knowledge with effective control methods can lead to a successful solution. Whether you’re using traps, bait stations, or professional services, taking action to manage mice can help ensure a rodent-free environment.
By recognizing the role of natural predators and employing effective control methods, we can maintain a balance that keeps mice at bay and protects our homes and businesses.